Create a relationship
A relationship helps you combine data from two different tables. In an Access desktop database, you can create a relationship in
the Relationships window. Creating a relationship in an Access app is a different process, as explained later under Create a relationship in an Access app.
-
On the Database Tools tab, in the Relationships group, click Relationships.
-
If you haven't yet defined any relationships, the Show Table dialog box automatically appears. If it doesn't appear, on the Design tab, in the Relationships group, click Show Table.
The Show Table dialog box displays all of the tables and queries in the database. To see only tables, click Tables.
-
Select one or more tables, and then click Add. After you have finished adding tables, click Close.
-
Drag a field (typically the primary key) from one table to the common field (the foreign key) in the other table. To drag multiple fields, press the Ctrl key, click each field, and then drag them.
The Edit Relationships dialog box appears.

-
Verify that the field names shown are the common fields for the relationship. If a field name is incorrect, click on the field name and select the appropriate field from the list.
-
To enforce referential integrity for this relationship, select the Enforce Referential Integrity box.
-
Click Create.
Access draws a relationship line between the two tables. If you selected the Enforce Referential Integrity check box, the line appears thicker at each end. In addition, again only if you selected the Enforce Referential Integritycheck box, the number 1 appears over the thick portion on one side of the relationship line, and the infinity symbol (∞) appears over the thick portion on the on the other side of the line.
NOTES
-
To create a one-to-one relationship Both of the common fields (typically the primary key and foreign key fields) must have a unique index. This means that the Indexed property for these fields should be set to Yes(No Duplicates). If both fields have a unique index, Access creates a one-to-one relationship.
-
To create a one-to-many relationship The field on the one side (typically the primary key) of the relationship must have a unique index. This means that the Indexed property for this field should be set to Yes(No Duplicates). The field on the many side should not have a unique index. It can have an index, but it must allow duplicates. This means that the Indexed property for this field should be set to either No or Yes (Duplicates OK). When one field has a unique index, and the other does not, Access creates a one-to-many relationship.
A relationship helps you combine data from two different tables. In an Access desktop database, you can create a relationship in
the Relationships window. Creating a relationship in an Access app is a different process, as explained later under Create a relationship in an Access app.
the Relationships window. Creating a relationship in an Access app is a different process, as explained later under Create a relationship in an Access app.
- On the Database Tools tab, in the Relationships group, click Relationships.

- If you haven't yet defined any relationships, the Show Table dialog box automatically appears. If it doesn't appear, on the Design tab, in the Relationships group, click Show Table.
The Show Table dialog box displays all of the tables and queries in the database. To see only tables, click Tables.
- Select one or more tables, and then click Add. After you have finished adding tables, click Close.
- Drag a field (typically the primary key) from one table to the common field (the foreign key) in the other table. To drag multiple fields, press the Ctrl key, click each field, and then drag them.
The Edit Relationships dialog box appears.

- Verify that the field names shown are the common fields for the relationship. If a field name is incorrect, click on the field name and select the appropriate field from the list.
- To enforce referential integrity for this relationship, select the Enforce Referential Integrity box.
- Click Create.
Access draws a relationship line between the two tables. If you selected the Enforce Referential Integrity check box, the line appears thicker at each end. In addition, again only if you selected the Enforce Referential Integritycheck box, the number 1 appears over the thick portion on one side of the relationship line, and the infinity symbol (∞) appears over the thick portion on the on the other side of the line.
NOTES
- To create a one-to-one relationship Both of the common fields (typically the primary key and foreign key fields) must have a unique index. This means that the Indexed property for these fields should be set to Yes(No Duplicates). If both fields have a unique index, Access creates a one-to-one relationship.
- To create a one-to-many relationship The field on the one side (typically the primary key) of the relationship must have a unique index. This means that the Indexed property for this field should be set to Yes(No Duplicates). The field on the many side should not have a unique index. It can have an index, but it must allow duplicates. This means that the Indexed property for this field should be set to either No or Yes (Duplicates OK). When one field has a unique index, and the other does not, Access creates a one-to-many relationship.
Create a relationship in an Access app
The Relationships window isn't available in an Access app. Instead of creating a relationship in an Access app, you create a lookup field that gets values from a related field in another table. For example, let’s say you have an Employees table and you want to add a lookup to a Regions table so you can show which region each employee works in.
NOTE The field that your lookup will use as the source for values must already exist before you create your lookup field.
Here’s how you create a lookup field:
-
Open the table where you want to create a new lookup field by double-clicking it in the navigation. (Hint: you may need to click Home > Navigation Pane to see the available tables.)
In the above example, click the Employees table.
-
Click in the Field Name column just below the last field in the table and type a name for your new lookup field.
In the example, type Region as the field name.
-
In the Data Type column, click the arrow and select Lookup.
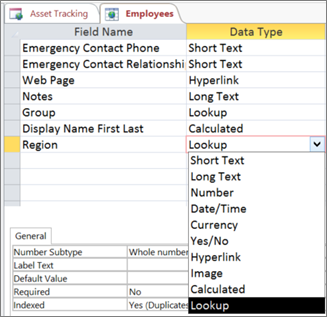
The Lookup Wizard starts.
-
On the first page of the Lookup Wizard, select I want the lookup field to get values from another table or query. More options appear in the dialog box.
-
Select the name of the table or query that should provide the values for your lookup.
In the example, select Table: Regions.
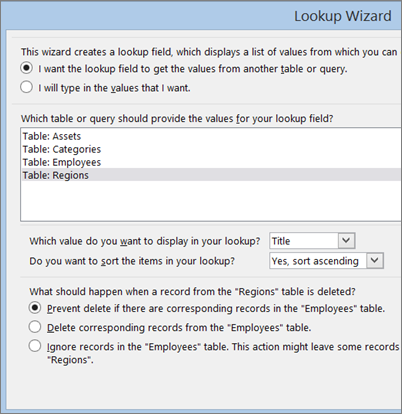
(Names of the tables in the image correspond to the example we’re using.)
-
After you select the table, use the Which value do you want to display in your lookup list to select the field that you want to use as a display value for your lookup field. By default, Access selects the first text field it can find in the selected table.
In the example, you would leave the selected field, Title, as the display value.
-
Use the Do you want to sort the items in your lookup list to set the sorting, if you want.
-
Under What should happen when a record from the “Regions” table is deleted, set the type of relationship you want between the two tables and whether you want to enforce referential integrity. (The name of the table in this question varies depending on which table you selected in step 5.)
The Lookup Wizard defaults to Prevent delete if there are corresponding records in the “Employees” table, because that’s the safest option in most cases. In the example, this option means you can’t delete a value from the Regions table if that region is being used in records in the Employees table. So, if employee records are using a region, such as “West” and you try to delete “West” from the Regions table, Access will prevent you from deleting it. In this case, you need to reset all employee records using that value to something else, before you can delete “West” from the Regions table. The last option could work in this example, because that would allow you to delete “West” from the Regions table. The region value would be automatically removed from Employee records that were set to “West,” leaving the value blank. Choosing the second option would delete all employee records from the Employees table that have the region set to “West.” That’s called a cascading delete and would delete much more data than you want in the example. Be careful when choosing that option.
The Relationships window isn't available in an Access app. Instead of creating a relationship in an Access app, you create a lookup field that gets values from a related field in another table. For example, let’s say you have an Employees table and you want to add a lookup to a Regions table so you can show which region each employee works in.
NOTE The field that your lookup will use as the source for values must already exist before you create your lookup field.
Here’s how you create a lookup field:
- Open the table where you want to create a new lookup field by double-clicking it in the navigation. (Hint: you may need to click Home > Navigation Pane to see the available tables.)
In the above example, click the Employees table. - Click in the Field Name column just below the last field in the table and type a name for your new lookup field.
In the example, type Region as the field name. - In the Data Type column, click the arrow and select Lookup.

The Lookup Wizard starts. - On the first page of the Lookup Wizard, select I want the lookup field to get values from another table or query. More options appear in the dialog box.
- Select the name of the table or query that should provide the values for your lookup.
In the example, select Table: Regions.

(Names of the tables in the image correspond to the example we’re using.) - After you select the table, use the Which value do you want to display in your lookup list to select the field that you want to use as a display value for your lookup field. By default, Access selects the first text field it can find in the selected table.
In the example, you would leave the selected field, Title, as the display value. - Use the Do you want to sort the items in your lookup list to set the sorting, if you want.
- Under What should happen when a record from the “Regions” table is deleted, set the type of relationship you want between the two tables and whether you want to enforce referential integrity. (The name of the table in this question varies depending on which table you selected in step 5.)
The Lookup Wizard defaults to Prevent delete if there are corresponding records in the “Employees” table, because that’s the safest option in most cases. In the example, this option means you can’t delete a value from the Regions table if that region is being used in records in the Employees table. So, if employee records are using a region, such as “West” and you try to delete “West” from the Regions table, Access will prevent you from deleting it. In this case, you need to reset all employee records using that value to something else, before you can delete “West” from the Regions table. The last option could work in this example, because that would allow you to delete “West” from the Regions table. The region value would be automatically removed from Employee records that were set to “West,” leaving the value blank. Choosing the second option would delete all employee records from the Employees table that have the region set to “West.” That’s called a cascading delete and would delete much more data than you want in the example. Be careful when choosing that option.
Relationship:-
- Is a kind of “attribute” which connect two or more than two tables is called “Relationship”.
We have three kind of Relationship which are given below.
1) One to One
2) One to Many
3) Many to Many
- Is a kind of “attribute” which connect two or more than two tables is called “Relationship”.
We have three kind of Relationship which are given below.
1) One to One
2) One to Many
3) Many to Many
One-to-One Relationship
Definition - What does One-to-One Relationship mean?
A one-to-one relationship in a relational database occurs when one parent record or field has either zero or one child record only. These relationships are the easiest to represent in databases because both the parent and child records may be in the same table.
One to One relationship:-
Number First we will work on One to One relationship that how we can make “Relationship” between One to One table and we will work on “Employee database” by the example of “One to One table”. With the help of one to one relationship we can divide a long table by two tables. To make a “relationship” between two tables follow these steps which are given below.
1) Start Microsoft Access 2007
2) Click on "Blank database" then give a name "Employee" and lastly click on "Create" button as given below.
3) Click on "Create" Menu and then click on "Table Design" command. As you will click on "Table Design" command after that fills your information after that take "Primary key" of ID. To take the "Primary key" of ID right Click on "ID" and then choose "Primary key" you can also get "primary key" from "Design" Menu which is given below.
Notes: What is different between Text and Memo in data type column?
Text: - Text is a field of “data type” which contains up to 255 characters in a cell or the length set by “field size” property and “Memo” is also a field of “data type” which contains up 63,999 character. Its mean that whenever a sentence or paragraph which can write more than 255 character than we use “Memo” like information.
4) Click on “View” command and then choose “Datasheet view” from “Design” or “Home” as given below.
5) Then click “yes” and type a name for example “Employee” and lastly click “OK”.
6) Close the table from “close” button or click “Ctrl+W” from keyboard
7) Again click on “Create” menu and then click on “table design”. Now fill the information in another table which is given below.
8) Again click on “View” command and choose “Datasheet View” from “Design” or from “Home” menu. After click on “Datasheet view” click “yes” and “type a name” for example “Employee 2” then click “OK” and lastly choose no primary key.
9) Also close it from “close” button or click “Ctrl+W” from keyboard.
10) Now go to “Database Tools” menu and click on “Relationships” command as given below.
11) As you will click on “Relationships” command choose both of table by the help of “Ctrl” button and then click “Add” as given below.
12) After click on “Add” button then click “Close”.
13) Now drag the first “ID” which has “Primary key” to another “ID” as given below.
14) After dragging of “ID” the three options will appear. Checkup the first one and then click on “Create” button as given below.
15) Now press “Ctrl+S” from keyboard to save it and then close the display of Relationship with the help of “Close” button or click “Ctrl+W” from keyboard.
16) Now Open the first table “Employee” with double clicks or right clicks on it and then chooses “open”. As you will open your “Employee” table fills it by your own information as given below.
17) Now as you will fill your information a “plus sign” will appear at the 1st cell of ID as given below.
18) Click on “plus” sign and then fill your information.
How to insert CV file?
Right click on the first cell of CV and then click on “Insert object” as given below.
19) As you will click on “Insert object” a menu will display click on “Create from file” option and then click on “Browse” button now select your CV file then click OK and lastly also click OK.
Now like this also insert your Picture in picture column and fill your other information as given below.
This was our tutorial about One to One relationship in database and I hope you like this tutorial
A one-to-one relationship in a relational database occurs when one parent record or field has either zero or one child record only. These relationships are the easiest to represent in databases because both the parent and child records may be in the same table.
One to One relationship:-
Number First we will work on One to One relationship that how we can make “Relationship” between One to One table and we will work on “Employee database” by the example of “One to One table”. With the help of one to one relationship we can divide a long table by two tables. To make a “relationship” between two tables follow these steps which are given below.
1) Start Microsoft Access 2007
2) Click on "Blank database" then give a name "Employee" and lastly click on "Create" button as given below.
3) Click on "Create" Menu and then click on "Table Design" command. As you will click on "Table Design" command after that fills your information after that take "Primary key" of ID. To take the "Primary key" of ID right Click on "ID" and then choose "Primary key" you can also get "primary key" from "Design" Menu which is given below.
Notes: What is different between Text and Memo in data type column?
Text: - Text is a field of “data type” which contains up to 255 characters in a cell or the length set by “field size” property and “Memo” is also a field of “data type” which contains up 63,999 character. Its mean that whenever a sentence or paragraph which can write more than 255 character than we use “Memo” like information.
4) Click on “View” command and then choose “Datasheet view” from “Design” or “Home” as given below.
5) Then click “yes” and type a name for example “Employee” and lastly click “OK”.
6) Close the table from “close” button or click “Ctrl+W” from keyboard
7) Again click on “Create” menu and then click on “table design”. Now fill the information in another table which is given below.
8) Again click on “View” command and choose “Datasheet View” from “Design” or from “Home” menu. After click on “Datasheet view” click “yes” and “type a name” for example “Employee 2” then click “OK” and lastly choose no primary key.
9) Also close it from “close” button or click “Ctrl+W” from keyboard.
10) Now go to “Database Tools” menu and click on “Relationships” command as given below.
11) As you will click on “Relationships” command choose both of table by the help of “Ctrl” button and then click “Add” as given below.
12) After click on “Add” button then click “Close”.
13) Now drag the first “ID” which has “Primary key” to another “ID” as given below.
14) After dragging of “ID” the three options will appear. Checkup the first one and then click on “Create” button as given below.
15) Now press “Ctrl+S” from keyboard to save it and then close the display of Relationship with the help of “Close” button or click “Ctrl+W” from keyboard.
16) Now Open the first table “Employee” with double clicks or right clicks on it and then chooses “open”. As you will open your “Employee” table fills it by your own information as given below.
17) Now as you will fill your information a “plus sign” will appear at the 1st cell of ID as given below.
18) Click on “plus” sign and then fill your information.
How to insert CV file?
Right click on the first cell of CV and then click on “Insert object” as given below.
19) As you will click on “Insert object” a menu will display click on “Create from file” option and then click on “Browse” button now select your CV file then click OK and lastly also click OK.
Now like this also insert your Picture in picture column and fill your other information as given below.
This was our tutorial about One to One relationship in database and I hope you like this tutorial












No comments:
Post a Comment